Das zu den Seltenen Erden und den Lanthanoiden zählende chemische Element Gadolinium tritt in der Natur ausschließlich in der 3-wertigen Form auf. Darüber hinaus sind Verbindungen mit dem zweiwertigen Gd(II)-Kation bekannt; diese besitzen jedoch keinerlei praktische Bedeutung.
Das Gadolinium-Ion ist in wäßriger Lösung farblos.
Während die gewöhnlichen Gadoliniumsalze so gut wie keine technischen oder sonstigen praktischen Anwendungen finden, haben verschiedene Gadoliniumkomplexe in der diagnostischen Medizin eine breite Anwendung als Kontrastmittel gefunden [vgl. weiter unten].
Tabelle: Gadolinium-Verbindungen
Die nachfolgende Übersicht zeigt die hier behandelten Verbindungen des Gadoliniums, insbosondere der Gadolinium-Salze, einige ihrer Eigenschaften und Verweise auf die Detail-Informationen, die im Anschluss an der Tabelle zu finden sind.
| Name | Formel | Molmasse | Fp. | Kp. | Dichte |
| Gadobensäure | C22H28GdN3O11 | 667,72 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadobutrol | C18H31GdN4O9 | 604,710 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadodiamid | C16H28GdN5O9 | 573,656 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadofosveset Trinatrium | C33H41GdN3O14P | 975,875 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadolinium(III)-acetat Tetrahydrat | C4H6GdO4 | 406,44 g mol-1 | Z °C | 1,61 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-bromid | GdBr3 | 396,96 g mol-1 | 770 °C | 4,56 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-chlorid | GdCl3 | 263,61 g mol-1 | 602 °C | 4,52 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-chlorid Hexahydrat | GdCl3 | 371,70 g mol-1 | 2,424 g cm-1 | ||
| Gadolinium(III)-fluorid | GdF3 | 214,25 g mol-1 | 1232 °C | ||
| Gadolinium(III)-iodid | GdI3 | 537,96 g mol-1 | 930 °C | ||
| Gadolinium(II)-iodid | GdI2 | 411,06 g mol-1 | 831 °C | ||
| Gadolinium(III)-nitrat Hexahydrat | Gd(NO3)3 | 451,36 g mol-1 | Z 91 °C | 2,33 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-nitrat Pentahydrat | Gd(NO3)3 | 433,34 g mol-1 | Z 92 °C | 2,41 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-oxalat Decahydrat | Gd(C2O4)3 | 758,71 g mol-1 | Z 100 °C | ||
| Gadolinium(III)-oxid | Gd2O3 | 362,50 g mol-1 | 2339 °C | 3900 °C | 7,41 g cm-1 |
| Gadolinium(III)-oxysulfid | Gd2O2S | 378,56 g mol-1 | 7,32 g cm-1 | ||
| Gadolinium(II)-selenid | GdSe | 236,21 g mol-1 | 2170 °C | 8,1 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-orthosilikat | Gd2SiO5 | 422,58 g mol-1 | 1900 °C | 6,71 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-sulfat | Gd2(SO4)3 | 602,69 g mol-1 | Z 500 °C | 4,1 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-sulfat Octahydrat | Gd2(SO4)3 | 746,81 g mol-1 | Z 400 °C | 4,14 g cm-1 | |
| Gadolinium(III)-sulfid | Gd2S3 | 410,70 g mol-1 | 6,1 g cm-1 | ||
| Gadolinium(III)-tellurid | Gd2Te3 | 697,30 g mol-1 | 1255 °C | 7,7 g cm-1 | |
| Gadopentetat-Dimeglumin | C28H54GdN5O20 | 938,00 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadopentetsäure | C14H18GdN3O10 | 547,575 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadoteridol | C17H29GdN4O7 | 558,68 g mol-1 | ca. 225 °C | ||
| Gadotersäure | C16H25GdN4O8 | 558,64 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadoversetamid | C20H34GdN5O10 | 661,77 g mol-1 | |||
| Gadoxetinsäure | C23H30GdN3O11 | 681,75 g mol-1 |
Gadolinium(II)-Verbindungen
Gadolinium(II)-iodid
Metallisch bronzefarbene, undurchsichtige, sehr hygroskopische Kristalle, die an der äußerst sehr instabil sind und nur unter Schutzgas verwendbar sind. Die Synthese gelingt durch Reduktion von Gadoliniumtriiodid im Vakuum bei 800 bis 900 °C.
Gadolinium(II)-selenid
Kubische, wasserunlösliche Kristalle.
Dichte: 8,1 g cm-3
Gadolinium(III)-Verbindungen
Gadolinium(III)-acetat Tetrahydrat
Weiße, trikline Kristalle mit ferromagnetischen Eigenschaften
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich
Dichte: 1,61 g cm-3
Gadolinium(III)-bromid
Hygroskopische, weiße, monokline Kristalle
Dichte: 4,56 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 75576; PubChem: 83754.
Gadolinium(III)-chlorid
Hygroskopische, weiße, monokline Kristalle
läßt sich durch Einwirkung von Salzsäure und metallischem Gadolinium herstellen
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich
Dichte: 4,52 g cm-3
Kristallstruktur: Raumgruppe P63/m Nr. 177; Gitterkonstanten a = 736,3 und c = 410,5 nm
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 55406; PubChem: 61486.
Gadolinium(III)-chlorid Hexahydrat
Hygroskopische, farblose, monokline Kristalle
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich
Dichte: 2,424 g cm-3
Kristallstruktur: Raumgruppe P2/n
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 171299; PubChem: 197915.
Gadolinium(III)-fluorid
Weiße Kristalle
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 75538; PubChem: 83716.
Gadolinium(III)-iodid
Gelbe Kristalle
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 83588; PubChem: 75418.
Gadolinium(III)-nitrat Hexahydrat
Hygroskopische, trikline Kristalle
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich: 1900 g/L (25 °C)
Dichte: 2,33 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 181304; PubChem: 209258.
Gadolinium(III)-nitrat Pentahydrat
Weiße Kristalle
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich: 1900 g/L (25 °C)
Dichte: 2,41 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 140078; PubChem: 159266.
Gadolinium(III)-oxalat Decahydrat
Weißes Pulver
Löslichkeit: wasserunlöslich, löslich in Säuren
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 150859; PubChem: 132965.
Gadolinium(III)-oxid
Weißes Pulver
Löslichkeit: wasserunlöslich, löslich in Säuren
Dichte: 7,41 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 140201; PubChem: 159427.
Gadolinium(III)-oxysulfid
Weißes Pulver
Verwendung als Szintillatormaterial, Verstärkersubstanz und in Leuchtstoffen (dotiert mit Eu, Pr, Tb)
Löslichkeit: unlöslich in Wasser
Dichte: 7,32 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 8018486; PubChem: 9842771.
Gadolinium(III)-orthosilikat
Szintillatormaterial für Detektoren in der Nuklearmedizin
Dichte: 6,71 g cm-3
Externe Daten: PubChem: 44150499.
Gadolinium(III)-sulfat
Farblose Kristalle
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich: 26 g/L
Dichte: 4,1 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 146004; PubChem: 166873.
Gadolinium(III)-sulfat Octahydrat
Farblose, monokline Kristalle
Löslichkeit: wasserlöslich: 23 g/L
Dichte: 4,14 g cm-3
Gadolinium(III)-sulfid
Gelbe, kubische Kristalle
Dichte: 6,1 g cm-3
Gadolinium(III)-tellurid
Orthogonale Kristalle
Dichte: 7,7 g cm-3
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 4891956; PubChem: 6336990.
Gadolinium-Kontrastmittel
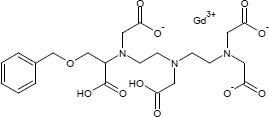
Gadobensäure
Gadobensäure ist ein Komplex von Gadolinium mit dem Liganden BOPTA. Es wird als Methylglucamin-Salz in der Magnetresonanztomographie als Kontrastmittel eingesetzt.
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA08 (Kontrastmittel für die Magnetresonanztomographie, MRT)
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 94843; PubChem: 6918204.
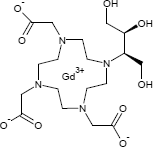
Gadobutrol
Gadobutrol ist ein Gadolinium-basiertes, hydrophiles, makrocyclisches, elektrisch neutrales Kontrastmittel, das in der kontrastverstärkten MRI (CE-MRI) eingesetzt wird.
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA09 (Kontrastmittel für die Magnetresonanztomographie, MRT)
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 28536137; PubChem: 72057.
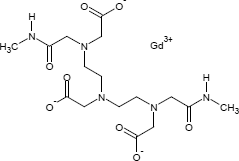
Gadodiamid
Paramagnetisches MRT-Kontrastmittel, dass als Monohydrat (CAS 122795-43-1) eingesetzt wird.
Löslichkeit: Gut in Wasser und Methanol; löslich in Ethanol, etwas in Aceton und Chloroform.
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA03 (Kontrastmittel für die Magnetresonanztomographie, MRT)
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 135661; PubChem: 153921.
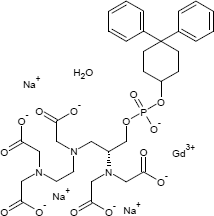
Gadofosveset Trinatrium
Ein auf Gadolinium basierendes MRI-Kontrastmittel, das als Monohydrat verwendet wurde. Der Hersteller (Lantheus Medical) stellte die Produktion 2017 aufgrund des schwachen Absatzes ein.
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA11 (Kontrastmittel für die Magnetresonanztomographie, MRT)
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 139381; PubChem: 46174086.
Gadopentetat-Dimeglumin
Dimegluminsalz der Gadopentetsäure, einem Chelatkomplex aus Gadolinium-Ionen und dem Komplexbildner Diethylentriaminpentaessigsäure (DTPA).
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA01 (Gadopentetsäure)
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 50087; PubChem: 55466.
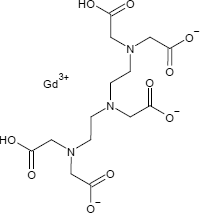
Gadopentetsäure
Chelatkomplex aus 9-fach koordinierten (3N, 5O, 1Wasser) Gadolinium-Ionen und dem Komplexbildner Diethylentriaminpentaessigsäure (DTPA); wurde als erstes paramgnetisches, intravenöses MRT-Kontrastmittel eingesetzt. Das Gadoliniumion hat 7 ungepaarte Elektronen mit parallelen Spins und ist stark paramagnetisch mit einem elektronischen s8-Grundzustand. Die Entspannungszeit der Wassermoleküle wird durch ihre intermittierende Bindung an das paramagnetische Zentrum beeinflusst. Dies ändert ihre MRI-Eigenschaften und ermöglicht so eine Kontrastverbesserung.
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA01 (Kontrastmittel für die Magnetresonanztomographie, MRT)
Externe Daten: PubChem: 6857474.
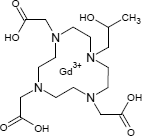
Gadoteridol
Weiße, Klümpchen bildende Kristalle. Verwendung in Form des optisch inaktiven Racemats
Löslichkeit: löslich in Wasser, Alkohol; schwer löslich in unpolaren Lösungsmitteln
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA04
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 54719; PubChem: 60714.
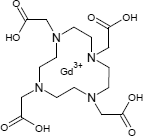
Gadotersäure
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA02
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 2342608; PubChem: 3085828.
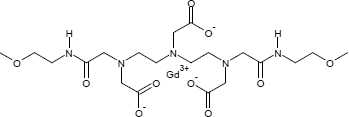
Gadoversetamid
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA06
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 392041; PubChem: 6435809.
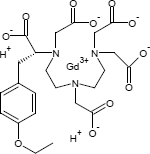
Gadoxetinsäure
ATC-Code (Wirkstoff): V08CA10
Externe Daten: ChemSpider: 189907; PubChem: 219084.
Gadolinium-Mineralien
Tabelle: Gadoliniumhaltige Mineralien, Zusammensetzung und prozentuale Anteile (berechnet als Prozent Atommasse an Molmasse).
| Mineral | Zusammensetzung | Kristallsystem | Molmasse | Prozent Gd |
| Monazit-(Sm) | SmPO4 ((Sm,Gd,Ce,Th)[PO4]) | monoklin | 221,25 g mol-1 | 14,21 % |
| Churchit-(Dy) | (Dy,Sm,Gd,Nd)(PO4) × 2 H2O | monoklin | 283,93 g mol-1 | 11,08 % |
| Schuilingit-(Nd) | PbCu(Nd,Gd,Sm,Y)(CO3)3(OH) × 1,5 H2O | orthorhombisch | 696,16 g mol-1 | 6,87 % |
| Mineevit-(Y) | Na25Ba(Y,Gd,Dy)2(HCO3)4(CO3)11(SO4)2ClF2 | hexagonal-dipyramidal | 2115,35 g mol-1 | 4,46 % |
| Decrespignyit-(Y) | (Y,SEE)4Cu(CO3)4Cl(OH)5 × 6 H2O | monoklin | 867,49 g mol-1 | 3,99 % |
| Caysichit-(Y) | Y2(Ca,Gd)2Si4O10(CO3)3(H2O,O,OH) × H3O | orthorhombisch-pyramidal | 819,17 g mol-1 | 3,84 % |
| Proshchenkoit-(Y) | (Y,SEE,Ca,Na,Mn)15FeIICa(P,Si)Si6B3(O,F)48 | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 2711,51 g mol-1 | 3,15 % |
| Zajacit-(Ce) | NaSEE0,5Ca0,5SEE0,25Ca0,75F6 | trigonal-rhombohedral | 295,08 g mol-1 | 2,88 % |
| Maoniupingit-(Ce) | (SEE,Ca)4(Fe+++,Ti,Fe++,[ ])(Ti,Fe+++,Fe++,Nb)4Si4O22 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1228,90 g mol-1 | 2,76 % |
| Aluminocerit-(Ce) | Ca2,6Ce2,49Nd1,62La0,8Sm0,44Pr0.38Gd0.3Y0.26Dy0.04Yb0.01Al0,85Fe3+0,1 (SiO4)3(SiO3)4(OH)4(OH)3,06 | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 1725,28 g mol-1 | 2,73 % |
| Calcybeborosilit-(Y) | (SEE,Ca)2[](B,Be)2(SiO4)2(OH,O)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 437,09 g mol-1 | 2,59 % |
| Levinsonit-(Y) | Y0,3Nd0,2La0,1Sm0,1Gd0,1Al(SO4)2(C2O4) × 12 H2O | monoklin-prismatisch | 623,48 g mol-1 | 2,52 % |
| Calciogadolinit | CaSEE(Fe+++)Be2Si2O10 | monoklin-prismatisch | 474,11 g mol-1 | 2,39 % |
| Kentbrooksit | (Na,SEE)15(Ca,SEE)6Mn++Zr3NbSi25O74F2 × 2 H2O | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 3900,86 g mol-1 | 2,32 % |
| Abenakiit-(Ce) | Na26SEE6(SiO3)6(PO4)6(CO3)6(S++++O2)O | hexagonal-scalenohedral | 2928,18 g mol-1 | 2,32 % |
| Hundholmenit-(Y) | (Y,SEE,Ca,Na)15(Al,FeIII)CaxAsIII1-x(Si,AsV)Si6B3(O,F)48 | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 2521,06 g mol-1 | 2,24 % |
| Hingganit-(Y) | Y2([ ])Be2Si2O8(OH)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 433,65 g mol-1 | 2,18 % |
| Percleveit-(Ce) | Ce0,87La0,41Nd0,35Y0,12Pr0,09Sm0,07Gd0,06Dy0,01Si2,01O7 | tetragonal-pyramidal | 442,72 g mol-1 | 2,13 % |
| Thomasclarkit-(Y) | (Na,Ce)(Y,SEE)(HCO3)(OH)3 × 4 H2O | monoklin-sphenoidal | 375,77 g mol-1 | 2,11 % |
| Pyatenkoit-(Y) | Na5(Y,Dy,Gd)TiSi6O18 × 6 H2O | trigonal-trapezohedral | 821,63 g mol-1 | 1,91 % |
| Lepersonnit-(Gd) | CaGd2(UO3)24(CO3)8(SiO4)4O4 × •60 H2O | orthorhombisch | 8909,01 g mol-1 | 1,84 % |
| Adamsit-(Y) | NaY(CO3)2 × 6 H2O | triklin-pinakoidal | 344,24 g mol-1 | 1,83 % |
| Kamotoit-(Y) | (Y,Nd,Gd)2U4(CO3)3O12 × 14,5 H2O | monoklin-prismatisch | 1790,08 g mol-1 | 1,76 % |
| Calcioburbankit | Na3(Ca,SEE,Sr)3(CO3)5 | dihexagonal-pyramidal | 597,04 g mol-1 | 1,71 % |
| Kozoit-(La) | (Nd,La,Sm,Pr)(CO3)(OH) | orthorhombisch-dipyramidal | 205,20 g mol-1 | 1,65 % |
| IMA2008-024 | (Ca,Na,SEE,[ ])7(Nb,Ti)[Si2O7]2OF3 | monoklin-domatisch | 841,27 g mol-1 | 1,34 % |
| Khristovit-(Ce) | (Ca,SEE)(Ce,SEE)(Mg,Fe,Cr,Ti,V,Al)MnIIAl(SiO4)(Si2O7)(OH)(F,O) | monoklin-prismatisch | 610,88 g mol-1 | 1,30 % |
| IMA2009-001 | Ba5(Ca,SEE,Y)22(Ti,Nb)18(SiO4)4[(PO4),(SiO4)]4(BO3)9O22[(OH),F]43 × 1,5 H2O | trigonal-pyramidal | 4586,47 g mol-1 | 1,23 % |
| Dissakisit-(Ce) | Ca(Ce,SEE)(Mg,FeII)(Al,FeIII)2Si3O12(OH) | monoklin-prismatisch | 599,36 g mol-1 | 1,23 % |
| Trimounsit-(Y) | (Y,SEE)2Ti2SiO9 | monoklin-prismatisch | 475,18 g mol-1 | 1,19 % |
| Hellandit-(Y) | (Ca,SEE)4(Y,Ce)2(Al,[ ])2[Si4B4O22](OH)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1029,47 g mol-1 | 1,10 % |
| Moskvinit-(Y) | Na2K(Y,SEE)[Si6O15] | orthorhombisch-dipyramidal | 598,41 g mol-1 | 1,05 % |
| Kamphaugit-(Y) | (Ca1,84SEEx)(Y1,46SEE0,54-x)(CO3)4(OH)1,65 × 2 H2O | tetragonal-trapezohedral | - g mol-1 | 1,04 % |
| Nioboaeschynit-(Y) | [(Y,SEE),Ca,Th,Fe](Nb,Ti,Ta)2(O,OH)6 | orthorhombisch-dipyramidal | 368,70 g mol-1 | 1,04 % |
| Hellandit-(Ce) | (Ca3SEE)4Ce2Al[ ]2[Si4 B4O22](OH)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1114,02 g mol-1 | 1,02 % |
| Iwashiroit-(Y) | - | monoklin-prismatisch | - g mol-1 | 1,00 % |
| Strontiochevkinit | (Sr,SEE)4Fe(Ti,Zr)2Ti2Si4O22 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1140,23 g mol-1 | 0,99 % |
| Gerenit-(Y) | (Ca,Na)2(Y,SEE)3Si6O18 × 2 H2O | triklin-pinacoidal | 872,18 g mol-1 | 0,97 % |
| Chukhrovit-(Nd) | Ca3(Nd,Y)Al2(SO4)F13 × 12 H2O | isometrisch-diploidal | 857,24 g mol-1 | 0,92 % |
| Bussyit-(Ce) | (Ce,SEE)3(Na,H2O)6MnSi9Be5(O,OH)30F4 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1329,21 g mol-1 | 0,92 % |
| IMA2009-005 | (Y,Ca,SEE)5[(Si,P)O4]3F | dihexagonal-dipyramidal | 696,25 g mol-1 | 0,81 % |
| Ciprianiit | Ca4[(Th,U)(SEE)]2(Al,[])2[Si4B4O22](OH,F)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1032,51 g mol-1 | 0,80 % |
| Paratooit-(La) | SEE3(Ca,Sr)2NaCu(CO3)8 | orthorhombisch-disphenoidal | 2146,77 g mol-1 | 0,73 % |
| Fluorcalciobritholit | (Ca,SEE)5[(Si,P)O4]3F | hexagonal-dipyramidal | 710,23 g mol-1 | 0,66 % |
| Uedait-(Ce) | - | monoklin-prismatisch | 584,87 g mol-1 | 0,54 % |
| Samarskit-(Y) | (Y,FeIII,U)(Nb,Ta)5O4 | orthorhombisch-dipyramidal | 299,85 g mol-1 | 0,50 % |
| Kuliokit-(Y) | (Y,SEE)4Al(SiO4)2(OH)2F5 | triklin-pedial | 706,82 g mol-1 | 0,48 % |
| Agardit-(Ce) | - | hexagonal-dipyramidal | 1070,95 g mol-1 | 0,44 % |
| Cerotungstit-(Ce) | (Ce,SEE)W2O6(OH)3 | monoklin-prismatisch | 655,80 g mol-1 | 0,43 % |
| Bijvoetit-(Y) | (Y,SEE)8(H2O)25(UO2)16O8(OH)8(CO3)16 × 14 H2O | monoklin-sphenoidal | 7068,68 g mol-1 | 0,32 % |
| Johnsenit-(Ce) | Na12(Ce,SEE,Sr)3Ca6Mn3Zr3W(Si25O73)(CO3)(OH,Cl)2 | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 3374,09 g mol-1 | 0,28 % |
| Mckelveyit-(Nd) | (Ba,Sr)(Ca,Na,Nd,SEE)(CO3)2 × 3-10 H2O | triklin-pinakoidal | - g mol-1 | 0,25 % |
| Georgbarsanovit | Na12(Mn,Sr,SEE)3Ca6FeII3Zr3NbSi25O76Cl2 × 6 H2O | trigonal, ditrigonal-pyramidal | 3297,19 g mol-1 | 0,22 % |
| Miserit | K1,5-x(Ca,Y,SEE)5[Si6O15][Si2O7](OH,F)2 × y H2O | triklin-pinacoidal | - g mol-1 | 0,22 % |
| Cerit-(La) | (La,Ce,Ca)9(Mg,Fe+++)(SiO4)6[SiO3(OH)](OH)3 | ditrigonal-pyramidal | 1825,93 g mol-1 | 0,17 % |
| Kapitsait-(Y) | (Ba,K,Pb,Na)4(Y,Ca,SEE)2[Si8B2(B,Si)2O28F] | triklin-pinacoidal | 1419,80 g mol-1 | 0,16 % |
| Mckelveyit-(Y) | NaCa(Ba,Sr)3(Y,SEE)(CO3)6 × 3 H2O | monoklin | 971,59 g mol-1 | 0,15 % |
| Vastmanlandit-(Ce) | (Ce,La)3CaAl2Mg2[Si2O7][SiO4]3F(OH)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 1094,51 g mol-1 | 0,14 % |
| Plumboagardit | (Pb,SEE,Ca)Cu6(AsO4)3(OH)6 × 3 H2O | hexagonal-dipyramidal | 1097,39 g mol-1 | 0,14 % |
| Piergorit-(Ce) | - | monoklin-prismatisch | 1498,89 g mol-1 | 0,10 % |
| Hingganit-(Ce) | Ce2Be2(SiO4)2(OH)2 | monoklin-prismatisch | 460,63 g mol-1 | 0,07 % |
| Dissakisit-(La) | (Ca,FeII,Th,La)(La,SEE,Ca)(Al,Cr,Ti)2(Mg,Fe,Al)Si3O12(OH,F) | monoklin-prismatisch | 551,33 g mol-1 | 0,03 % |
Eine Liste aller Seltenerd-Mineralien mit den prozentualen Anteilen der einzelnen Seltenerdmetalle am jeweiligen Mineral findet man unter Seltenerd-Mineralien.
Kategorie: Stoffgruppen
Letzte Änderung am 27. Juni 2023.
Permalink: https://www.internetchemie.info/chemie-lexikon/stoffgruppen/gadolinium-verbindungen.php.
© 1996 - 2026 Internetchemie ChemLin